History does not often give the satisfaction of a sudden and lasting turning point. History tends to unfold in messy cycles—actions and reactions, revolutions and counterrevolutions—and even semipermanent changes are subtle and glacial. But the rise of religious non-affiliation in America looks like one of those rare historical moments that is neither slow, nor subtle, nor cyclical. You might call it exceptional.
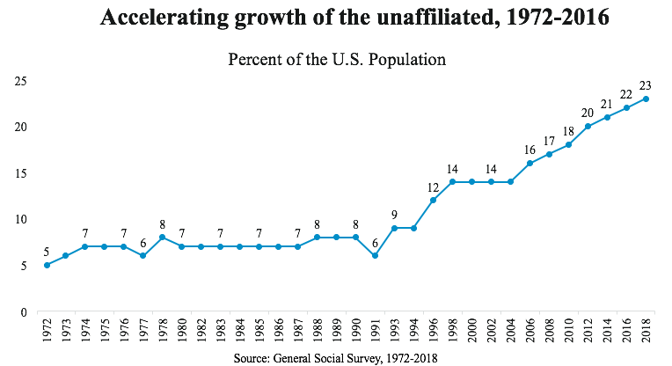
The obvious question for anybody who spends at least two seconds looking at the graph above is: What the hell happened around 1990? According to Christian Smith, a sociology and religion professor at the University of Notre Dame, America’s nonreligious lurch has mostly been the result of three historical events: the association of the Republican Party with the Christian right, the end of the Cold War, and 9/11.
This story begins with the rise of the religious right in the 1970s. Alarmed by the spread of secular culture—including but not limited to the sexual revolution, the Roe v. Wade decision, the nationalization of no-fault divorce laws, and Bob Jones University losing its tax-exempt status over its ban on interracial dating—Christians became more politically active. The GOP welcomed them with open arms. The party, which was becoming more dependent on its exurban-white base, needed a grassroots strategy and a policy platform. Within the next decade, the religious right—including Ralph Reed’s Christian Coalition, James Dobson’s Focus on the Family, and Jerry Falwell’s Moral Majority—had become fundraising and organizing juggernauts for the Republican Party. In 1980, the GOP social platform was a facsimile of conservative Christian views on sexuality, abortion, and school prayer.
The marriage between the religious and political right delivered Reagan, Bush, and countless state and local victories. But it disgusted liberal Democrats, especially those with weak connections to the Church. It also shocked the conscience of moderates, who preferred a wide berth between their faith and their politics. Smith said it’s possible that young liberals and loosely affiliated Christians first registered their aversion to the Christian right in the early 1990s, after a decade of observing its powerful role in conservative politics.
